What types of durable barcode labels are used in the Medical industry?
The need for ACCURACY and DURABILITY permeates every facet of the Medical industry – after all, lives depend on it.
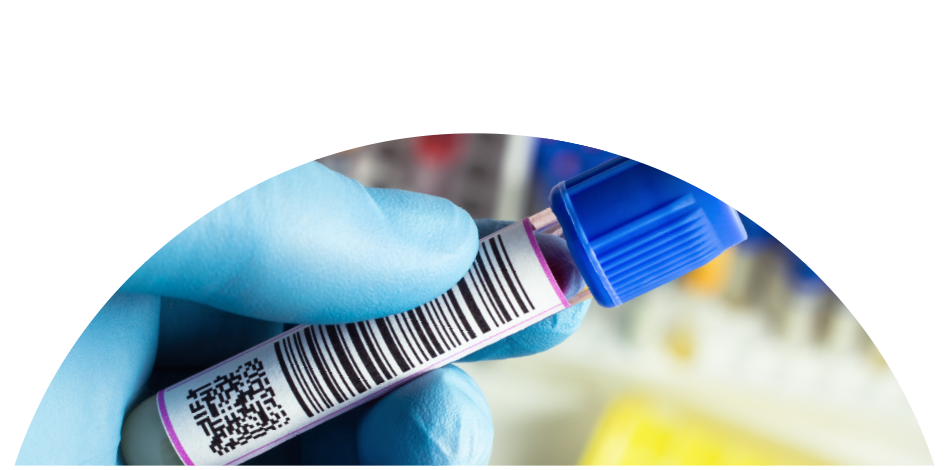
2D medical barcoding such as QR codes and Data Matrix (GS1) labels offer a secure, accurate and reliable method for data storage in healthcare. Across a wide range of medical applications, 2D barcoding can accommodate more information in a smaller amount of space than its predecessor, 1D barcoding. Hospitals, pharmaceutical providers, laboratories and device manufacturers are using 2D barcoding technology in a variety of ways.
Larger Data Capacity for 2D Medical Barcoding
Both QR codes and Data Matrix (GS1) labels feature the ability to expand data storage capacities for medical institutions and device manufacturers. Medical providers employ different internal processes, and as such, have to implement a barcoding solution that can be tailored to their needs based on data size, physical barcode size, data integrity, data density and damage resistance. Whether tracking blood samples in a phlebotomy lab or the sterilization of surgical equipment, each department will have its own set of data requirements.
Composed of squares, rectangles and/or small dot patterns, 2D barcodes not only increase the amount of data storage in a smaller physical size, but they also contain redundancy features that reduce errors during scanning. They retain their readability in challenging conditions, are more secure, and can be quickly scanned via smart phone by any doctor, nurse, lab technician or records manager. 2D barcode patterns can also be permanently etched into medical equipment.
Popular 2D Barcodes for Healthcare
QR Codes
QR codes are among the most commonly used types of 2D barcodes, allowing for up to 2,509 numeric or 1,520 alpha-numeric characters. The size of the actual image can be scaled to accommodate anything from test tubes to defibrillator units. QR codes are ubiquitous in almost every industry, from aerospace to food & beverage. With QR codes, healthcare providers can greatly expand their ability to accurately and securely manage data across various departments, unified to a single barcode standard with built-in features that prevent errors. QR codes can connect various healthcare data to smartphones, tablets, medical devices and other systems with a single Android or iOS app.
Data Matrix
Data Matrix labels offer even greater options for data density, survivability and error prevention. Capable of storing up to 3,116 characters, these square patterned grids can be scanned in virtually any orientation. In addition, it’s possible for scanners to still be able to read the label even when damaged thanks to its integrated error prevention features. For healthcare industries, Data Matrix labels are especially vital to supply chain management for medical devices, supporting and tracking a product’s lifecycle from manufacturing to daily use.
Additional Advancements in Medical 2D Barcoding
RFID Tags and Barcoding
RFID tags are already being deployed for the medical device industry, providing both active and passive data reading for various healthcare management applications. Medical equipment can now be tracked within or outside a facility via RFID tags. This provides an array of other advantages including maintenance and calibration records or medical device data billing. It also reduces the time it takes for caregivers to search for equipment throughout a facility, resulting in lower operational costs. It is common to find RFID tags and 2D barcoding labels working together for different processes.
Blockchain Technology and Medical Barcoding
Blockchain Technology utilizes cryptographic software methods for storing medical data, thereby preventing modification or tampering. As more healthcare organizations embrace blockchain applications, 2D barcodes can be employed in tags, labels and wristbands to help ensure the secure facilitation of data across devices, departments and networks. While the technology is relatively new, securing barcode data on the blockchain is already underway.
2D Barcoding Improves Healthcare Processes
In 2011, the Food & Drug Administration issued guidance for the application of 2D barcodes, including UDI & GS1. The Center for Disease and Control provides a brief overview for adopting 2D barcodes into existing healthcare processes.
Both QR Codes and Data Matrix labels offer a diverse range of possibilities for the healthcare industry. This includes asset tracking, patient record management, medical supplies inventory, lab specimen samples and much more. 2D barcodes offer a versatile toolset that allows medical facilities and device manufacturers to integrate secure, efficient and cost effective data management processes.
Durability makes all the difference
Barcode labels in the Medical field must stand up to all types of severe environments. Why? Because the data contained MUST be protected. When you think about it, Medical environments can be surprisingly injurious:
- Gurneys take abuse during patient transport.
- ICU room temperatures vary from cold to warm.
- Sterile labs and surgical environments use harsh cleansers.
- Monitoring equipment is regularly moved throughout the facility.
- Expensive diagnostic equipment requires tamper-proof barcode labels.












